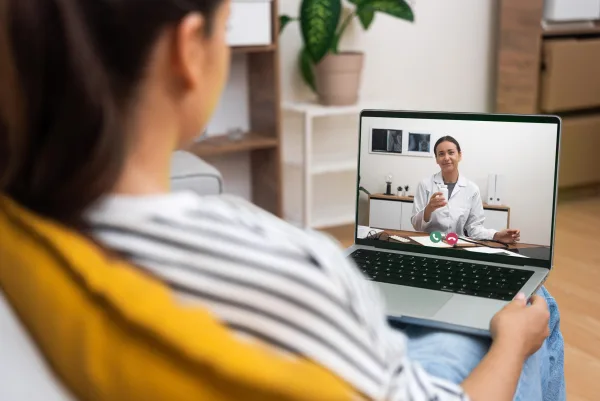
HIPAA compliance for telehealth is a growing operational challenge for healthcare organizations. As telehealth and telemedicine expand, providers must protect health information while delivering care through remote communication technologies that were not originally designed for regulated healthcare environments.
Scale adds complexity. Telehealth services often span state lines, rely on multiple telehealth platforms, and involve providers holding numerous licenses. Each factor introduces compliance risk when verification, credentialing, or monitoring processes are incomplete or outdated. For covered entities and health plans, HIPAA compliance for telehealth depends on ensuring the right providers have appropriate access, supported by accurate, verified data.
In this environment, HIPAA and telehealth are closely linked. Protecting patients’ protected health information depends on both secure technology and reliable provider data verification.
Why HIPAA Compliance Matters in Telehealth
HIPAA compliance matters in telehealth because virtual care environments fundamentally change how sensitive data is accessed, transmitted, and stored. Telehealth services rely on communication technologies that transmit individually identifiable health information across networks, devices, and locations that often fall outside traditional clinical settings.
The HIPAA Privacy Rule and HIPAA Security Rule both apply when healthcare providers deliver care through telehealth technology. Together, these HIPAA rules establish expectations for privacy and security, including how covered health care providers protect health information when using remote communication technologies for telehealth.
When HIPAA requirements are not met, organizations may face:
- Increased security risk to protected health information
- Audit findings or investigations by the Office for Civil Rights
- Penalties for HIPAA violations and corrective action plans
Provider verification also plays a critical role. Inaccurate licensure data or incomplete credentials can allow unauthorized access to telehealth platforms, electronic health records, or systems that transmit protected health information when using telehealth services. These gaps became more visible during the covid-19 public health emergency, when the Department of Health and Human Services applied enforcement discretion for telehealth remote communications.
As enforcement discretion ended, many organizations were required to come into compliance with the HIPAA privacy and security rules, reinforcing the need for defensible, repeatable verification practices.
Key Components of a HIPAA-Compliant Telehealth Program
A HIPAA-compliant telehealth program is built on more than secure video tools. It combines privacy safeguards, verified provider data, and operational workflows that help organizations comply with HIPAA consistently as telehealth services scale.
Mature programs align HIPAA guidelines with real-world workflows so providers, systems, and telehealth platforms support privacy and security without slowing the delivery of healthcare.
Multi-State License Verification and Monitoring
Telehealth providers often practice across state lines, holding multiple licenses to provide telehealth services in different jurisdictions. Tracking these licenses manually introduces significant compliance risk, especially as provider networks expand.
Accurate, real-time primary-source verification helps organizations:
- Confirm providers are authorized to practice telehealth in each state
- Prevent access by providers with expired or restricted licenses
- Reduce risk associated with unauthorized data access
Healthcare license verification supports HIPAA compliance by ensuring license data remains accurate and current. Ongoing monitoring further helps organizations identify changes in license status before they escalate into broader HIPAA compliance issues.
Credentialing and Eligibility Confirmation
Credentialing is often viewed as an administrative function, but it plays a direct role in HIPAA compliance for telehealth. Credentialing confirms provider identity, qualifications, and eligibility, supporting HIPAA-aligned access controls across telehealth platforms and health information technology systems.
In telehealth environments, this extends beyond individual providers to include vendor credentialing compliance, particularly when third parties support telehealth platforms, data transmission, or remote communication technologies that handle protected health information.
When credentialing data is incomplete or outdated, organizations may struggle to comply with HIPAA rules for telehealth. This increases privacy and security risks and complicates audit preparation.
Workforce management for healthcare supports HIPAA-aligned operations by helping ensure:
- Only authorized providers can access telehealth platforms
- Eligibility status is continuously validated
- Credentialing gaps are identified before they create compliance exposure
Secure Data Handling and Documentation
HIPAA compliance for telehealth also depends on how data is handled once care is delivered. Telehealth platforms must support encryption, secure transmission, and controlled access to protect health information when using remote communication technologies.
The HIPAA Security Rule requires covered entities to implement administrative, physical, and technical safeguards, including:
- Encryption and access controls
- Audit trails documenting system access
- Documentation retention to support HIPAA audits
Maintaining clear audit trails and consistent documentation also supports healthcare compliance audit preparation, helping organizations demonstrate adherence to HIPAA privacy and security requirements during reviews by the Office for Civil Rights or other oversight bodies.
Automated Compliance Workflows
Automation plays a critical role in HIPAA compliance for telehealth as organizations scale virtual care programs. Manual processes for license tracking, credentialing, and background screening increase the likelihood of human error and delay response times.
Automated workflows help organizations:
- Reduce gaps caused by manual data entry
- Accelerate onboarding for telehealth providers
- Apply HIPAA privacy and security rules consistently
This approach aligns with healthcare compliance monitoring, where continuously monitored data supports timely response to changes that could affect HIPAA compliance.
Over time, these practices illustrate the broader benefits of a compliance program in healthcare, including improved governance, reduced operational friction, and greater confidence when scaling telehealth services across states and care settings.
Common Mistakes Telehealth Organizations Make
Even experienced telehealth organizations encounter HIPAA compliance challenges as programs grow. Many issues stem from outdated assumptions rather than lack of effort.
Common mistakes include:
- Failing to track multi-state license expirations across telehealth providers
- Relying on manual systems that create compliance gaps
- Overlooking credentialing as a HIPAA-critical process
Left unaddressed, these gaps can escalate into audit findings, HIPAA violations, or broader healthcare legal issues that affect patient trust, operational continuity, and long-term telehealth strategy.
Questions to Ask When Evaluating Telehealth Compliance Solutions
When evaluating solutions to support HIPAA compliance for telehealth, organizations should focus on defensibility and scalability, not just features.
Key questions include:
- How do you verify providers holding multiple licenses across states?
- What safeguards protect PHI during credentialing and onboarding?
- How is data updated and monitored over time?
- What reporting supports HIPAA compliance audits?
Clear answers to these questions help organizations reduce compliance risk while maintaining efficient telehealth operations.
Strengthening Telehealth Compliance With Reliable Verification
HIPAA compliance for telehealth depends on more than secure technology. It requires accurate licensure, verified credentials, and workflows designed to protect health information while supporting care delivery at scale.
Organizations that prioritize verified data, automation, and ongoing monitoring are better positioned to protect patients’ protected health information, reduce privacy and security risks, and maintain compliance as telehealth programs evolve.
This is where Verisys provider data compliance solutions support healthcare organizations. Through solutions such as Healthcare Compliance Monitoring, Healthcare Background Screening, and Healthcare License Verification, Verisys helps large-scale telehealth networks maintain consistent, verified provider data that supports HIPAA compliance, operational efficiency, and long-term confidence.